| Cancer Stem Cell Markers |
| Cancers |
Markers |
| Breast |
CD29, CD49, CD49f, CD90, CD61, CD133, CD44, CD24, ALDH, ALDH1A1, BMI-1, Connexin 43/GJA1, CXCR4, DLL4, GLI-1, GLI-2, IL-6R, PON1, PTEN, Sox2, LGR5 |
| Prostate |
EpCAM, CD117, α2β1, ALDH, CD44, CD151, EZH2, CXCR4, ABCG2, ALCAM/CD166, ALDH1A1, c-Maf, c-Myc, TRA-1-60(R) |
| Brain |
CD49f, CD90, CD44, CD36, EGFR, A2B5, L1CAM, CD133 |
| Stomach |
ALDH, CD44, CD133, CD24, CD54, CD90, CD49f, CD71, EpCAM, DLL4, LGR5 |
| Colorectal |
CD200, CD133, CD166, CD206, CD44, CD49f, ALDH, EpCAM, CD24, ALDH1A1, DPP-4/CD26/DPPIV, LGR5, Musashi 1/MSI1 |
| Liver |
CD24, CD133, CD13, CD44, CD206, OV-6, CD90, EpCAM, Alpha-fetoprotein, Merlin/NF2 |
| AML |
CD34, CD38, CD90, CD71, CD19, CD20, CD44, CD10, CD45RA, CD123 |
| Melanoma |
CD20, CD271, ALDH, CD133, CD166, ABCB5, BCRP/ABCG2, NGFR/p75NTR, Nestin, MAGEA1, MAGEA3 |
| Bladder |
CD44v6, CD44, ALDH, CD47, CEACAM-6/CD66c |
| Pancreas |
ALDH, CD133, CD44, CD24, CD184, EpCAM, ABCG2, CXCR4, BMI1, PON1 |
| Head and Neck |
ALDH, CD44, CD166, BCRP/ABCG2, BMI1, LGR5, c-MET/HGFR |
| Lung |
CD166, CD90, CD87, ALDH, CD44, CD133, BCRP/ABCG2, c-Kit, Oct-3/4 |
| Ovarian |
AMACR, CD44, CD105, CD117 |
| Glioma /Medulloblastoma |
A20, CD44, CD133, CD15, CD49f, ABCG2, ALDH1A1, BMI-1, CX3CL1, CX3CR1, CXCR4, EPAS1, IL-6RA, L1CAM, c-Maf, c-Myc, SOX2 |
| Osteosarcoma |
CD44, CD105, BCRP/ABCG2, Nestin, STRO-1 |
| Myeloma |
CD138, CD19, CD27, CD38, CD20, ABCB5 |
| Cancer Stem Cell Transcription Factors |
| FoxM1, FoxO3, FRA-1, GLI-1, GLI-2, GLI-3, c-Jun, JunB, KLF4, c-Maf, MCM2, MCM7, β-Catenin, CREB, NR3A1, NR3A2, NR3C4, HIF1A, EPAS1, HIF3A, c-Myc, NFκB1, SOX2, SOX9, Oct-3/4, STAT3, TAZ, WT1, MITF, HMGA1B, PRDM14, p53, Twist-1, Twist-2, NKX3.1, TBX3, Snail, ZEB1 |


 Fig.1 Proposed models for CSC origin in cancer development.1
Fig.1 Proposed models for CSC origin in cancer development.1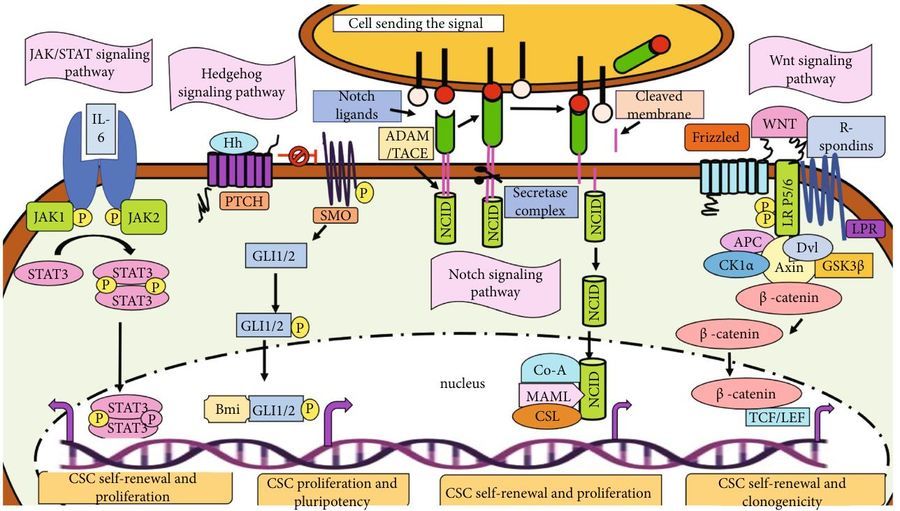 Fig.2 Signaling pathways involved in CSCs.2
Fig.2 Signaling pathways involved in CSCs.2

