-
-
Overview
-
3'5'-difluoro-4-hydroxybenzylidene imidazolinone (DFHBI) is a non-fluorescent small molecule that resembles the chromophore of green fluorescent protein (GFP). Upon binding to the "Spinach™" aptamer, DFHBI is converted to a highly fluorescent state that can be detected at the emission wavelength of 501 nm. DFHBI is cell permeable with negligible toxicity in living cells. DFHBI can be used to label any genetically encoded Spinach™ family of RNA tags that include Spinach™, Spinach2™, and Broccoli™. Live-cell imaging of tagged RNA can be performed using a standard fluorescence microscopy. Further, DFHBI can also selectively detect tagged RNA in total RNA gel electrophoresis. Thus, bypassing the need for Northern blot analysis.
Data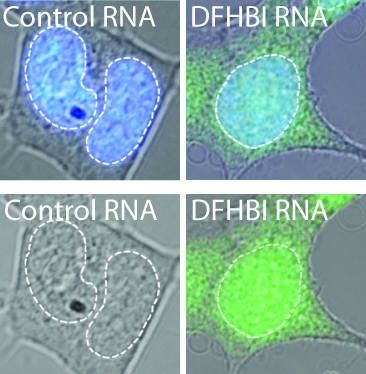
Figure 1. HEK293T cells were transfected with either 5S-control aptamer or 5S-Spinach™ plasmids and incubated with 20 µM DFHBI. Images are phase overlay with Hoechst-stained nuclei (blue) and Spinach™ fluorescence (green).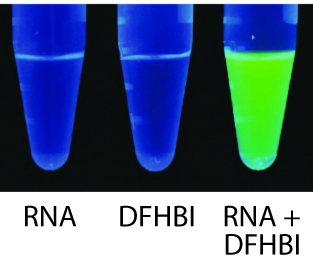
Figure 2. Spinach™ RNA robustly activates the fluorescence of DFHBI. Each tube contained the indicated solution and was irradiated at 465 nm.Please contact us at for specific academic pricing.
More Details
-
- Properties
- Applications
- Reference
-
Overview

- Home
- Products
- Life Science
- Analytical Chromatography
- Assay Kits
- Biochemical Reagents
- Antibodies
- Antigens
- Enzymes
- Chemicals
- Proteins
- Liposomes
- Cell Culture
- Cell Analysis
- Cloning and Expression
- Nucleic Acid Synthesis
- Nucleic Acid Extraction
- Nucleic Acid Electrophoresis
- PCR
- Protein Gel Electrophoresis
- Protein Biochemistry
- Nanoparticles
- Glycan Analysis
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Microbiology
- Biospecimens
- Transfection Reagents
- Ion Exchange Resins
- Venoms
- Lab Solutions
- Lab Equipment
- Biosensors
- Flow Imaging Microscopes
- Fluorescence Quality Management Solutions
- Electrophoresis Systems
- Hematology Analyzers
- Isothermal Amplification Instruments
- Liquid Handling Equipment
- Luminometers
- Microfluidic Flow Control Systems
- Next-generation Sequencing Systems
- Nucleic Acid Purification Instruments
- Raman Spectroscopy Systems
- Sample Tracking Systems
- Spectrometer Accessories
- Syringe Pumps
- Thawing and Warming Systems
- Tissue Dissociation Systems
- Water Purification Systems
- Western Blotting Equipment
- General Laboratory Equipment
- Clinical Chemistry Analyzers
- Amerigo Scientific Instrument
- Automated Cell Selection Systems
- Automated Nucleic Acid Extraction Instruments
- Balances, Scales and Weighing
- Biolayer Interferometry Instruments
- Bioprocess Filtration Equipment
- Bioprocess Systems and Accessories
- Bioreactors and Fermenters
- Cappers and Decappers
- Cell Thawing Instruments
- Chromatography
- Data Loggers
- Droplet Generators
- Dry Baths
- Flow Cytometers
- Histology Laboratory Equipment
- Lab Ovens and Furnaces
- Lab Refrigeration Equipment
- Lab Shakers and Mixers
- Laboratory Centrifuges
- Laboratory Evaporators
- Laboratory Hoods
- Laboratory Incubators
- Laboratory Microscopes
- Laboratory Mills
- Laboratory Pumps
- Liquid Handling
- Live Cell Imaging Systems
- Microbiology Equipment
- Microscopy Flow Cells
- Mutation Breeding Instruments
- Oligonucleotide Synthesis Devices
- Particle Counters
- Plasma Surface Treatment Equipment
- Presses and Pellet Dies
- Surface Plasmon Resonance Instruments
- Ultrasonic Cleaners
- UV Disinfection Systems
- VOC Analysis Equipment
- VPHP Sterilization Systems
- Water Baths
- Lab Equipment
- Diagnostics & Clinical
- Applied Science
- Life Science
- Services
- About Us
- Contact Us





![3-((1H-benzo[d]imadazol-4-yl)methyl)-5-(3,5-difluoro-4-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-methyl-3,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one ( BI )](https://resource.amerigoscientific.com/p-img/BI-2.png)


